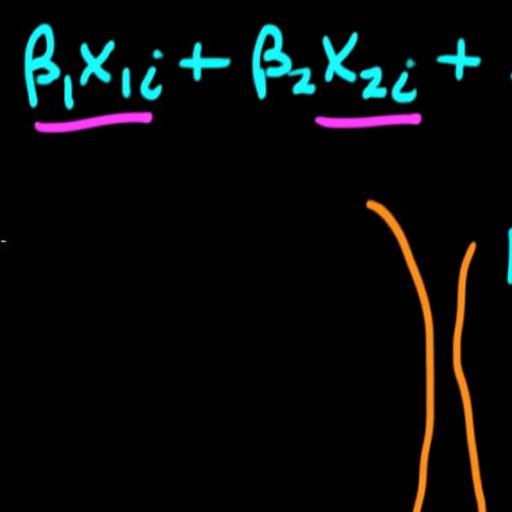Temporal aggregation poses many interesting questions which have been explored in time series analysis and which yet remain to be explored. An early example of research in this area is Quenouille (1957), where the temporal aggregation of ARIMA processes is studied. Amemiya and Wu (1972), and Brewer (1973) review and generalize Quenouille's result by including exogenous variables. Zellner and Montmarquette (1971) discuss the effects of temporal aggregation on estimation and testing. Engle (1969) and Wei (1978) analyze the effects of temporal aggregation on parameter estimation in a distributed lag model. Granger (1987) discusses the implications of aggregation on systems with common factors. Other contributions in this area include Tiao (1972), Stram and Wei (1986), Weiss (1984), Granger and Lee (1999), and Marcellino (1999), to name but a few.
In this paper, we examine the impact of temporal aggregation on the dynamic analysis and the forecasting properties of a stable ARIMA(p,q) process. There is a sizable theoretical literature that investigates the impact of temporal aggregation on ARIMA models (see Wei, 1990, and references therein).These studies are theoretical and focus on the effects of temporal aggregation on the orders p an q of the ARIMA process. This study using Monte Carlo simulation techniques, focus on the effects of using different selection criteria on the dynamic impulse responses and the forecasting properties of a stable ARMA process estimated at 16 different aggregation levels.